What Happens When FMCSA Comes to Audit Your Driver Logs?
Federal Motor Carrier Compliance Investigations (what you might remember as a Compliance Review) are still ongoing even during the COVID-19 pandemic – albeit virtually. And even though electronic logging devices have been mandatory for most fleets since last December, some companies find they may run into some trouble during one of these safety audits.
No matter what the type of investigation, he said, safety investigators must check the following areas during a compliance investigation, using the acronym CAIR (pronounced “care):
- CDL
- Authority
- Insurance
- Red Flag Violations
Recently added was the Drug and Alcohol Clearinghouse. In any type of investigation, the investigator looks at things such as whether the company is registered for the clearinghouse and if the company is doing the full clearinghouse queries before the driver gets behind the wheel.
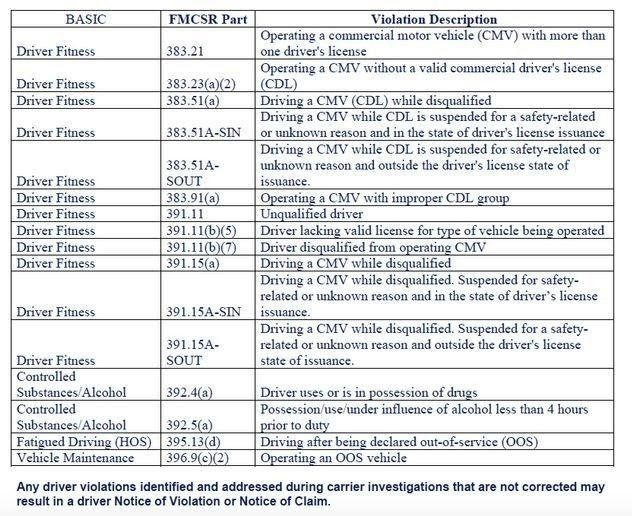
There are 16 “red flag” violations, where if an investigator discovered them during or prior to investigation, he or she is supposed to investigate what the company did in response – did they fire the driver, for instance. Examples include operating a truck without a valid CDL, driving after being declared out of service, or operating while using or in possession of drugs.
How Are ELD Records Audited?
There are two elements, a pre-investigation component, and the actual investigation of the records.
In the pre investigation, a safety inspector has to verify that ELDs are required by the company, and that its ELDs meet the requirements of the ELD rule. He or she also confirms that the ELD data can be retrieved electronically and can be transmitted to the investigator, either on site into the laptop, or if it’s an off-site audit, through the portal. The investigator uses a set formula to determine how many drivers and ELD records will be audited, as well as which drivers and ELD records will be audited. The formula requires them to review at least 30 records of duty status per driver. For off-site audits, the driver sample is much more limited – for instance, for an on-site review of a fleet with 100 drivers subject to the FMCSRs, they would have to select 11 drivers; for an off-site review, only three.
However, those drivers are not chosen at random, nor does the fleet get to pick its most compliant drivers for the review. Compliance officers will look for drivers with a red-flag violation, with the highest percentiles in the HOS BASIC, drivers involved in crashes, drivers with the highest violation rates, drivers with poor CDLIS driving records, recently hired drivers, and the highest-paid drivers.
The auditor then provides the company with a list of which drivers’ ELD data is being requested and give the company a link to upload that data. The inspector reviews the ELD data for compliance, and requests and reviews supporting documents, such as toll receipts, fuel reports, bills of lading, pay records, and scheduling records.
That’s all the pre-investigation. During the actual compliance investigation itself, there are two components: The basic review of ELD records and the review for falsification.
“The basic review really is about, are there hours of service violations,” Osiecki explained. “In the review for falsification, they look deeper to see if there are ways the driver is fudging the electronic record.”
In the basic review, investigators will:
- Interview key personnel to understand the fleet’s operations. How do company personnel book and plan dispatch and oversee the movement of the freight? They may follow up with accounts receivable and payroll. “They’re going to try to understand the process from the booking of the freight to the completed trip and the transfer of information,” Osiecki said.
- Interview drivers to get their perspective how the process works and to see if it matches up with the story from operations.
- Request various back-office reports from the ELD system, such as unassigned driving miles, the edit reports; odometer jump reports, and violation reports.
- Review each change of duty status on the graph grid and check it against the ELD record detailed data, looking for violations of the 11-hour, 14-hour, 60/70-hour, and 30-minute break rule. This is less time-consuming than it used to be, Osiecki noted, as investigators can use ERODS software that flags possible trouble spots instead of having to plow through paper logbooks.
- Check for unassigned driving miles and ask for explanation if none is provided.
- Check the edits report.
- Investigate ELD records, checking for system malfunctions or data diagnostics to determine if there’s an impact on hours of service.
And that’s just the “basic review.”
Fleets should keep in mind that there are hundreds of types of ELDs on the market and the investigator isn’t going to know the ins and outs of all of them. The investigators may not be familiar with the reports your system generates, so they’re going to lean on the company to educate them a little bit. Have patience with the investigator.”
Looking for cheating
While electronic logging devices may be harder to cheat than paper logs, that doesn’t mean fleets aren’t responsible for overseeing them. In fact, during a FMCSA session last year, the most commonly cited ELD violation in investigations was the motor carrier failing to ensure the driver’s ELD record was accurate. Other common violations were the motor carrier failing to electronically product ELD records upon request, and failing to review records of unidentified driving time and/or annotate the record explaining why the time was unassigned.
One of the common things’ investigators look for in digging for ELD cheating is the same driver using different logins, or not logging in. They will review the list of login IDs and the login activity and they also will look at unassigned driving time.
They also will verify that the on-duty location matches the location where the driver went off-duty, to check that the vehicle was not moved while the driver was off-duty (or allegedly in the sleeper berth.) If these locations are different, and the driver does not have a team driver, that ELD record may be false.
The 30-minute break is another common place where investigators find non-compliance issues. Under current rules, drivers must take an off-duty 30-minute break after eight hours on-duty. The safety investigator will compare the odometer reading at the beginning and end of that break to identify any movement that would break the rules that even under the new Sept. 29 revisions require drivers to be in non-driving status during their mandatory break.
Personal conveyance is the most common source of false log violations, so the investigator will check for off-duty/PC driving activity and ensure it adheres to FMCSA guidance. Beginning and ending odometer values may identify excessive distance that points to a need to dig further into that personal conveyance use.
Investigators will verify annotations and edits to make sure edits are done for justified reasons, and will check the edited versions against the original. As the training manual notes, Falsification may occur when driver edits on-duty/not-driving time to off-duty or sleeper time. This is the new way drivers falsify their log.
Another thing that many fleets may not think about: Investigators will look at the ELD support system setting to make sure there aren’t any features that allow fleets to customize settings in a way that would violate the rules – such as increasing the 5 mph threshold where the ELD automatically puts the driver in on-duty driving status, or disabling the volume being muted during sleeper berth time.
The investigator will review malfunction and diagnostic codes that could point to possible tampering, or to a carrier’s failure to address malfunctions and repair ELDs as required.
Finally, the investigator will compare the electronic logs to the supporting documents, such as fueling records. Supporting documents must be filed in a way that allows for easy matching to ELD records by compliance investigators.
Be Prepared
Three tips for fleets to prepare for an ELD investigation:
- Make sure your ELD records are organized and accessible.
- Create and follow an internal auditing system for hours of service and ELD records, including setting out how often it will be done, how many drivers and records will be checked, what ELD system reports to use, what ELD supporting documents to use, login activity and personal conveyance and yard moves checks, and making sure the ELDs communicate with the web portal for transferring data to law enforcement.
- Consider getting outside eyes to conduct a mock audit/investigation consistent with FMCSA procedures. There are a number of consulting companies that can do this.
- You can count on the NorthAmerican Transportation Association (www.ntassoc.org or www.ntassoc.com ) to keep you up-to-date. Our Members Only Portal is packed with valuable articles of interest to keep you out of trouble with State and/or Federal Agencies.
Content Disclaimer: Due to the constantly changing nature of government regulations, it is impossible to guarantee the total and absolute accuracy of the material contained herein or presented. NorthAmerican Transportation Association (NTA) cannot and does not assume any responsibility for omissions, errors, misprinting or ambiguity contained. NTA shall not be held liable in any degree for any loss, damage or injury caused by any such omission, error, misprinting or ambiguity present. It is made available with the understanding that NTA is not engaged in rendering legal, accounting or other professional service. If legal advice or other expert service is required, the services of such a professional should be sought.